Researchers Develop a Novel High Energy-Density Aqueous Battery
The recent years have seen a growing development of the aqueous batteries featuring high safety, low cost, and excellent rate performance. However, they are facing great challenges for large scale applications due to their low working voltage and energy density, which are caused by the narrow electrochemical window of aqueous electrolyte (1.23V) and low specific capacities of traditional intercalation-type electrodes.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. LIU Yu and CHI Xiaowei from Shanghai Institute of Ceramics innovatively proposed a high-energy-density (1503 Wh kg-1 calculated from the cathode active material) aqueous battery system achieved by dual dissolution/deposition reactions separated in acid-alkaline electrolyte. An acid-alkaline dual electrolyte separated by an ion-selective membrane expands the electrochemical window of electrolyte to 3 V successfully, which also enables two dissolution/deposition electrode redox reactions of MnO2/Mn2+ and Zn/Zn(OH)42- with theoretical specific capacities of 616 mAh g-1 and 820 mAh g-1, respectively.
The newly proposed Zn-Mn2+ aqueous battery shows high coulombic efficiency of 98.4% and cycling stability of 97.5% of discharge capacity retention for 1500 cycles. Furthermore, the excellent stability of 99.5% of discharge capacity retention for 6000 cycles is achieved in the flow battery based on the Zn-Mn2+ pairs.
Related research result was published in Advanced Energy Materials (2020, DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201903589) and selected to be featured on the inside cover of the journal. This work provides a new approach for the development of novel aqueous batteries with high voltage and energy density.
The first author of this work is LIU Chang, a PhD student from Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, and his supervisor is Prof. LIU Yu. This work was supported by relevant projects of the Ministry of Science and Technology and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
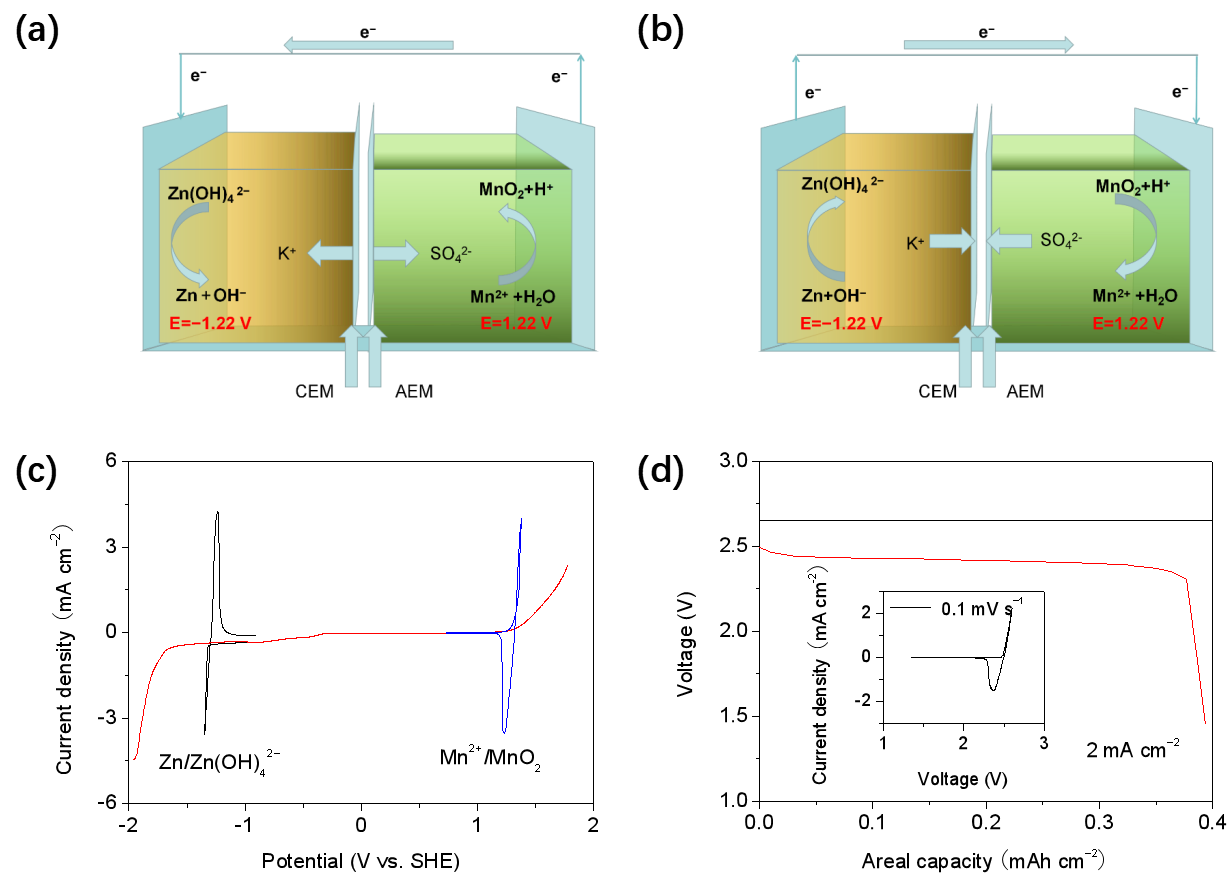
The schematic illustration and mechanism of Zn-Mn2+ battery using an acid-alkaline dual electrolyte

Electrochemical performance of the Zn-Mn2+ battery
Contact:
Prof. LIU Yu
Shanghai Institute of Ceramics
yuliu@mail.sic.ac.cn