SICCAS Made Progress on Microwave Properties of (Ba,Sr)TiO3 Thin Films
(Ba,Sr)TiO3(BST) thin films are being widely investigated for applications as Gbit dynamic random access memories, bypass capacitor, and tunable microwave devices because of its high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, good thermal stability, and good high frequency characteristics.
Recently, two research groups from Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SICCAS) and Institutd’Electronique, de Microélectronique, et de Nanotechnologie (IEMN) have made progress on microwave properties of BST60/40 thin films jointly. Perfectly (001)- and (111)-oriented BST thin films were directly grown on Pt(111)/TiOx/SiO2/Si substrates without any buffer layers were obtained. The O2/(Ar+O2)mixed ratios during deposition were found to have significant effects on the crystallographic orientation, microstructure and dielectric properties of BST films. Moreover, a low loss Bi1.5Zn1.0Nb1.5O7(BZN) was introduced to combine with perfectly BST(111) films to develop materials for tunable device applications with low dielectric losses, while still maintaining moderate tunablity. High tunability of 50%, low dielectric loss of 0.011 and a significant improvement in the figure of merit of 46.8 was obtained for BZN/BST composite films at 10 kHz and 400 kV/cm bias field.
To test BST thin films for practical purpose, the material should be characterized at microwave frequencies. Epitaxial (111)-oriented BST thin films on Al2O3(0001) substrates have been grown by inserting an ultrathin TiOx seeding layer. The dielectric dispersion demonstrated that the complex permittivity (ε=ε’-ε”) is well described by a Curie-von Scheidler power law with an exponent of 0.40. Moreover, the high permittivity (~428) combined with a high tunabilty 40.88% up to 40GHz suggest that epitaxial (111)-oriented BST thin film could be well suited for tunable microwave devices.
This achievements have been reported by the website of PhysOrg as “For future chips, smaller must also be better”, and the related work has been published in journals of Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 162909 (2010)、J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 350 (2010)、J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 1215 (2010)、J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 2136 (2010) and J. Am. Ceram.Soc. 93, 2526 (2010).This work was financially supported by National Basic Research Program (no. 61363Z09.1).
Related Links:http://nanotechwire.com/news.asp?nid=10696
http://www.physorg.com/news205490400.html
http://link.aip.org/link/?APL/97/162909
http://www.wiley.com/bw/journal.asp?ref=0002-7820
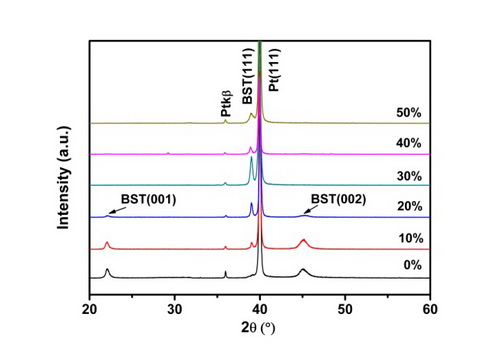
XRD patterns of BST thin films deposited with various oxygen pressure
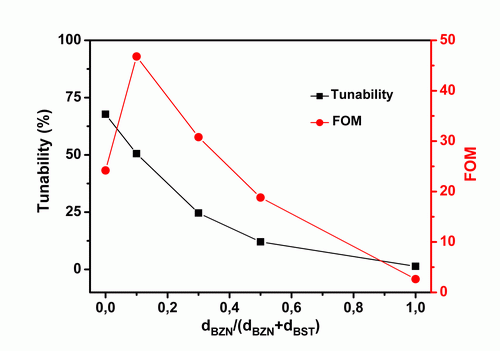
BZN thickness dependent tunability and FOM of the BZN/BST composite thin films
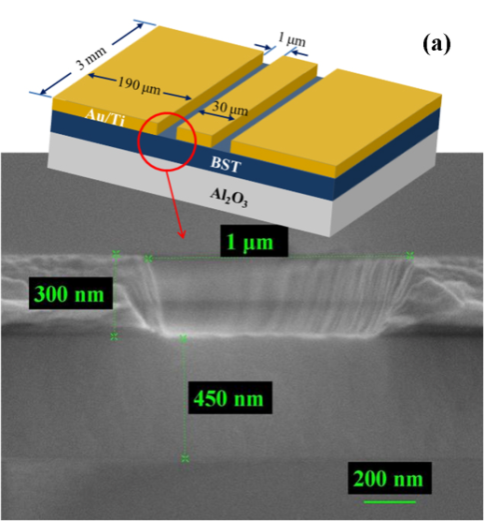
The coplanar waveguide transmission line structure for microwave measurement
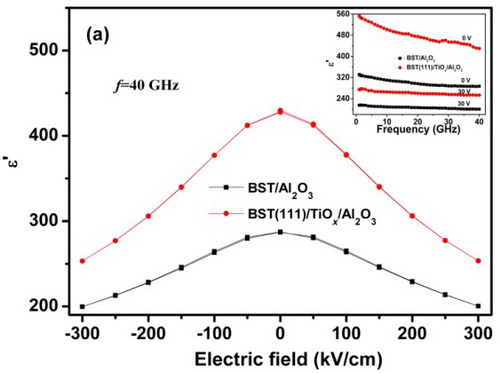
The microwave properties of epitaxial and polycrystalline BST films on sapphire up to 40GHz